Fitting 2D data¶
We will start by doing some necessary imports:
from astropy.modeling.astro_sherpa import SherpaFitter
from astropy.modeling.models import Gaussian2D
import numpy as np
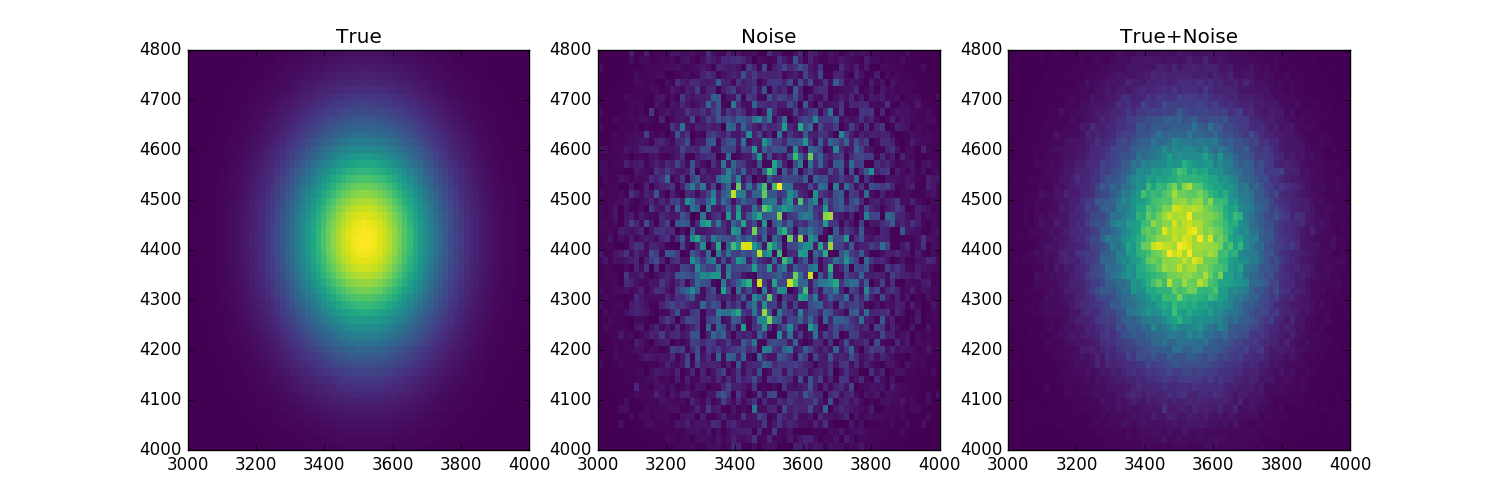
We need to define some data so we use the Gaussian2D model and add some poisson noise:
np.random.seed(123456789)
x0low, x0high = 3000, 4000
x1low, x1high = 4000, 4800
dx = 15
x1, x0 = np.mgrid[x1low:x1high:dx, x0low:x0high:dx]
shape = x0.shape
truth = Gaussian2D(x_mean=3512, y_mean=4418, x_stddev=150, y_stddev=150,
theta=20, amplitude=100)
mexp = truth(x0, x1).reshape(shape)
merr = abs(np.random.poisson(mexp) - mexp)
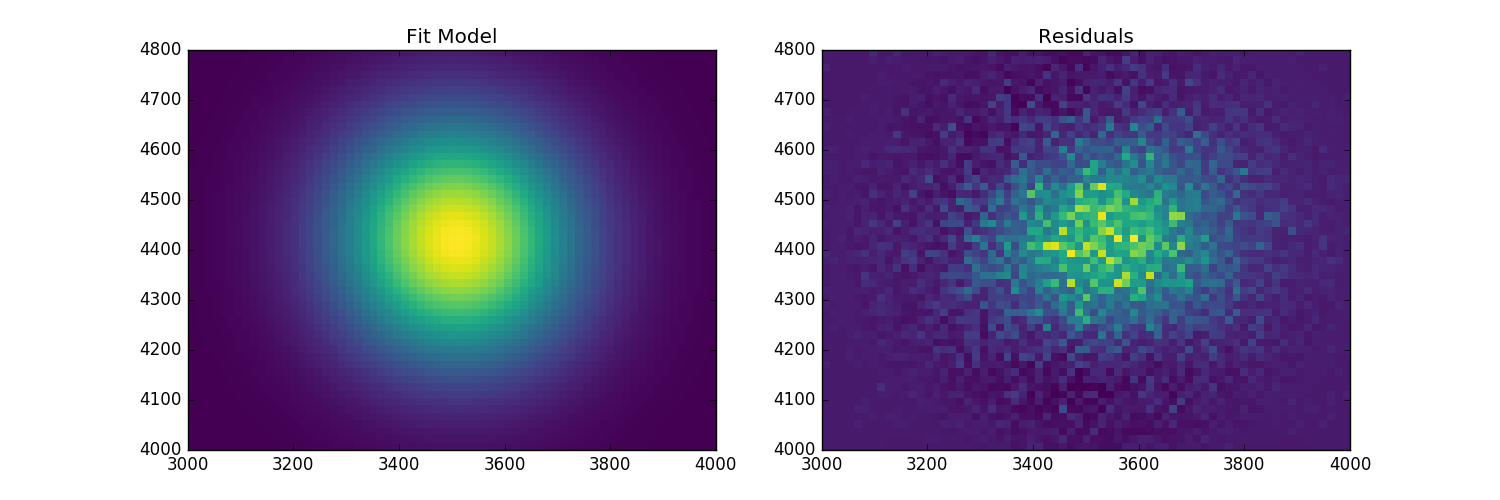
Now we have some data so let’s fit a model after the parameters have been offset. Here we flatten the arrays and then adjust the error bars for the fit:
sfit = SherpaFitter(statistic=Chi2)
fitmo = truth.copy()
fitmo.x_mean = 3650
fitmo.y_mean = 4250
fitmo.x_stddev = 100
fitmo.y_stddev = 100
fitmo.theta = 10
fitmo.amplitude = 50
fitmo = sfit(fitmo, x=x0.flatten(), y=x1.flatten(), z=mexp.flatten()+merr.flatten(),
xbinsize=np.ones(x0.size)*dx, ybinsize=np.ones(x1.size)*dx,
err=merr.flatten()+np.random.uniform(-0.5,0.5,x0.size))